Do you look for 'covalent bond homework'? Here you can find the questions and answers on the subject.
Table of contents
- Covalent bond homework in 2021
- What is true about covalent bonds
- Ionic and covalent bonding worksheet pdf
- Bonding practice worksheet answers
- Ionic and covalent bonding worksheet answers
- Covalent bond practice worksheet answers
- Ionic and covalent bonds practice worksheet answer key
- Covalent bonding quiz
Covalent bond homework in 2021
 This image demonstrates covalent bond homework.
This image demonstrates covalent bond homework.
What is true about covalent bonds
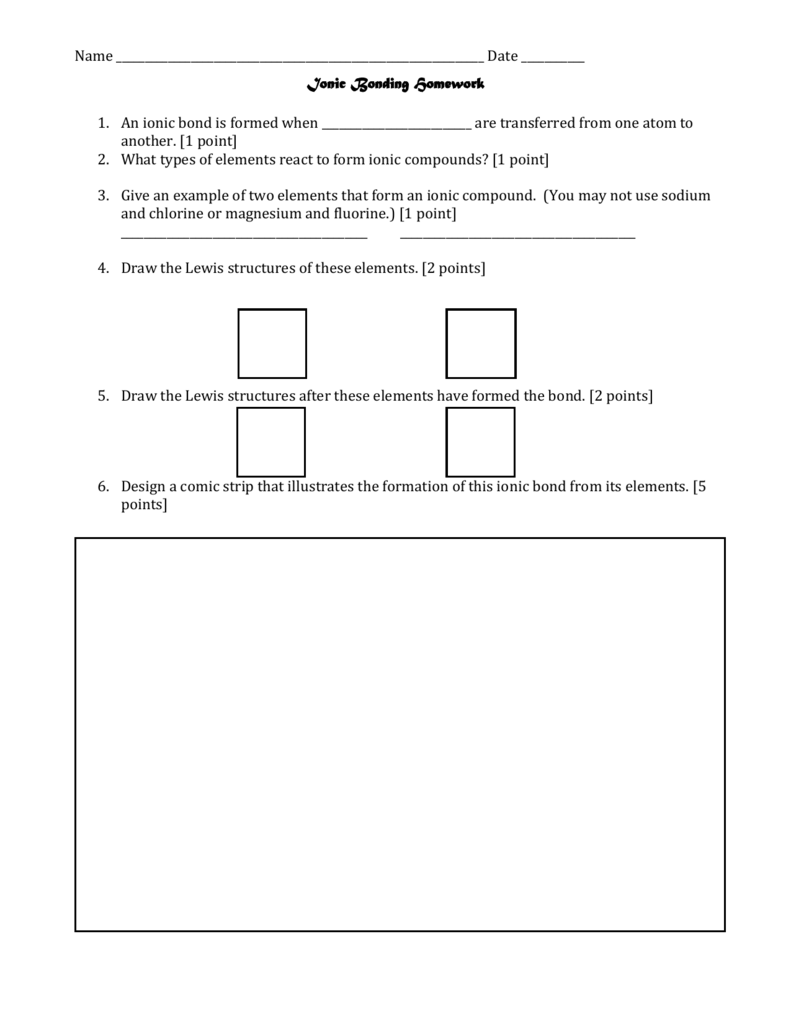 This picture demonstrates What is true about covalent bonds.
This picture demonstrates What is true about covalent bonds.
Ionic and covalent bonding worksheet pdf
 This image demonstrates Ionic and covalent bonding worksheet pdf.
This image demonstrates Ionic and covalent bonding worksheet pdf.
Bonding practice worksheet answers
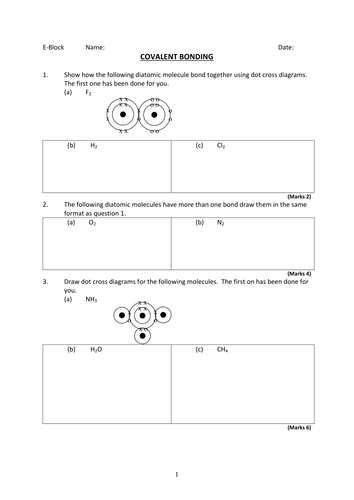 This picture illustrates Bonding practice worksheet answers.
This picture illustrates Bonding practice worksheet answers.
Ionic and covalent bonding worksheet answers
 This image demonstrates Ionic and covalent bonding worksheet answers.
This image demonstrates Ionic and covalent bonding worksheet answers.
Covalent bond practice worksheet answers
 This image demonstrates Covalent bond practice worksheet answers.
This image demonstrates Covalent bond practice worksheet answers.
Ionic and covalent bonds practice worksheet answer key
 This image representes Ionic and covalent bonds practice worksheet answer key.
This image representes Ionic and covalent bonds practice worksheet answer key.
Covalent bonding quiz
 This picture representes Covalent bonding quiz.
This picture representes Covalent bonding quiz.
Which is stronger a covalent bond or a single bond?
It is represented by two dashes (=). Double covalent bonds are much stronger than a single bond, but they are less stable. Example: Carbon dioxide molecule has one carbon atom with six valence electrons and two oxygen atom with four valence electrons.
What makes a bond nonpolar or polar covalent?
Whether a bond is nonpolar or polar covalent is determined by a property of the bonding atoms called electronegativity. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. It determines how the shared electrons are distributed between the two atoms in a bond.
How are the electrons in a covalent bond written?
Electron dot structures of covalent molecules are written with respect to the octet rule . According to this rule, all the atoms in the molecule will have eight electrons in their valence shell except the Hydrogen atom. Hydrogen will have only two electrons because only two electrons complete its first shell to attain helium configuration.
What are the absolute values of electronegativity in covalent bonding?
The absolute values of the electronegativity differences between the atoms in the bonds H–H, H–Cl, and Na–Cl are 0 (nonpolar), 0.9 (polar covalent), and 2.1 (ionic), respectively. The degree to which electrons are shared between atoms varies from completely equal (pure covalent bonding) to not at all (ionic bonding).
Last Update: Oct 2021